Simple S N 2 reaction. The reaction between a CC double bond and bromine Br 2 can be used as a test for the presence of alkene in an unknown sample.

Scheme 4 A Reaction Of Cyclohexene With Electrogenerated Bromine In Download Scientific Diagram
A chain reaction mechanism for the chlorination of methane was described earlier.
. Propylene oxide cyclohexane andor 2-methyl-2-butene are added as stabilizers. Figure 81b E2 Reaction Mechanism. The product is cyclohexane and the heat of reaction provides evidence of benzenes thermodynamic stability.
Then the two identical methyl groups are either cis or trans to each other and the two identical hydrogen atoms are either cis or trans to each other. For more than 40 years Flinn has been the Safer Source for Science. The bromine reagent is in a reddish color and the product vicinal dibromide is colorless.
The base OH uses its electron pair to attack a β-hydrogen on β-carbon and starts to form a bond. Bromine monoxide anion BrO Bromine monoxide cation C v. The 10 is the use of octanedioic acid sebacic acid instead of hexanedioic acid adipic acid in the reaction with the amine 16-diaminohexane hexamethylenediamine.
A demonstration of bromine substitution and addition reactions is helpful at this point. The E2 mechanism is also a single-step concerted reaction similar to S N 2 with multiple electron pair transfers that happen at the same time. Consisting all single bonds.
The ambiguity comes from the definition of similar groups. S N 1 and S N 2. The reaction rates were measured by using cyclohexane k H and cyclohexane-d 12 k D as substrates fig.
A KIE value of 112 k H k D was determined from parallel reactions 25 which indicated that the CHCD activation by Cl was not involved in the turnover-limiting step. Substrate structure controls substitution mechanism S N 1 or S N 2. S N 2 Reaction.
At the same time the β C-H sigma bond begins to move in to become the π bond of a double bond and. Bromine and iodine with this demonstration. Bromination of alkanes occurs by a similar mechanism but is slower and more selective because a bromine atom is a less reactive hydrogen abstraction agent than a chlorine atom as reflected by the higher bond energy of H-Cl than H-Br.
The Hofmann rearrangement Hofmann degradation is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one fewer carbon atom. C 4 H 4 N 2. Purity depends on the amount of C2 and higher hydrocarbons in the methane and the extent of chlorination.
BrF-bromine fluoride anion. One such development has been the production of polyamides which are made at least in part from renewable raw materials. Allyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Reaction.
What stereoisomers are obtained from the reaction of each of the following alkenes with OsO 4 followed by aqueous H 2 O 2. S N 2 examples. Reaction mass of 2-chloroethyl chloropropyl 2-chloroethylphosphonate mixture reaction mass of isomers and 2-chloroethyl chloropropyl 2-chloropropylphosphonate reaction mass of isomers 401-740-0 015-144-00-X reaction mass of pentyl methylphosphinate and 2-methylbutyl methylphosphinate 402-090-0 87025-52-3 015-145-00-5.
The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. Show how the energy of a chemical reaction can be given out as light by revealing how a solution of sodium chlorateI oxidises an aqueous solution of luminol 3-aminophthalhydrazide to produce a blue chemiluminescent glow without any increase in temperature. The cis-trans definition is unambiguous only when you have two different groups on one of the alkene carbons and the same two groups on the other carbon as in but-2-ene.
When bromine is added to the sample if the reddish color disappears it means the sample contains an alkene. Substituted benzene rings may also be deduced in this fashion and hydroxy-substituted compounds such as phenol catechol and resorcinol give. Stability and structure of carbocations.
2 o Benzyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Mechanism. Flinn Scientific is the 1 source for science supplies and equipment both in and outside the classroom. Methylene Chloride is derived from the chlorination of methane during which other chlorinated methane derivatives may be formed.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atomsThe term unsaturated means more hydrogen atoms may be added to the hydrocarbon to make it saturated ie. Includes kit list and safety. C 6 H 12 1R2R-12-dimethylcyclobutane.
An example is the production of polyamide 610. C 6 H 12 Z-hex-3-ene. The configuration of an unsaturated carbons include straight chain such as alkenes and alkynes as well as branched.
Benzyl Chloride with HS S N 2 Reaction. The reaction can form a wide range of products including alkyl and aryl amines.

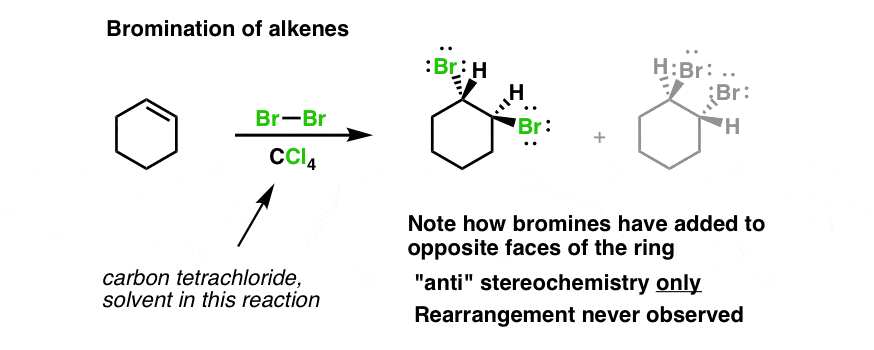
Bromination Of Alkenes Master Organic Chemistry
Properties Of Hydrocarbons Mendelset

Organic Chemistry Product Of Reaction Between Cyclohexene And Bromine In Methanol At 273 K Chemistry Stack Exchange
Reaction Of Bromine With Cyclohexane Cyclohexene And Benzene
0 Comments